


A 29-year-old woman presented following root canal therapy on tooth No. 4. Digital radiographs were taken using a photostimulable phosphor plate (ScanX, Air Techniques), which showed appropriate fill and no periapical radiolucency (Figure 1). The tooth was temporized with a temporary filling material and cotton pellet on presentation. A core buildup and crown were recommended as ideal definitive treatment. The patient consented to the proposed treatment, and no anesthesia was required.
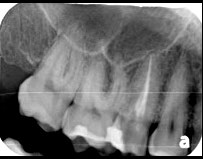
Figure 1—Radiograph of tooth No. 4 on presentation.
Removing the Temporary
The temporary material and residual caries were removed by using a Microcopy NeoDiamond 0512MS pear-shaped, short shank diamond bur (Figure 2). Using a phosphoric etch, universal adhesive, and a core buildup material, a buildup of No. 4 was completed (Figure 3). Due to the amount of remaining tooth structure, no post was required to retain the buildup. After the core material was allowed to fully cure, No. 4 was ready for crown preparation.
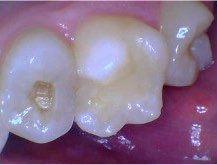
Figure 2—After tooth No. 4 was temporized, the temporary material and residual caries were removed with NeoDiamond 0512MS pear-shaped, short shank diamond bur.
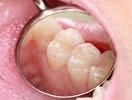
Figure 3—Tooth No. 4 post buildup and prior to preparation. Contacts were broken using a NeoDiamond 0512MS. Depth cuts were made using a NeoBurr 331 carbide bur.
Preparing the Tooth
The tooth was prepared using a sequence of Microcopy burs. Contacts were broken using the NeoDiamond 0512MS bur (Figure 3). Occlusal depth cuts were then made using a NeoBurr 331 carbide (Figure 3). This is an effective bur for generating appropriate reduction due to its cutting length of 1.8 mm.
An egg-shaped NeoDiamond 1900F was used to complete the occlusal reduction and connect the depth cut lines, and a NeoDiamond 0816.6CS flat-end taper shorty diamond was used to create a circumferential margin (Figure 4). A NeoDiamond round-end taper shorty diamond was used to complete the preparation and create a chamfer margin. A NeoDiamond 1900F and a NeoDiamond 3314.10VF very fine grit pointed-cone finishing bur were used to remove sharp edges and corners prior to impression taking. These Microcopy diamonds allowed for an easily attainable smooth and clear preparation (Figure 5). Retraction paste (Traxodent, Premier Dental) was used both as a hemostatic agent and to provide soft-tissue retraction prior to the digital impression. An intraoral scanner(TRIOS 4, 3Shape) was used to take digital impressions of the preparation and opposing arch, as well as to confirm appropriate reduction (Figures 6 & 7). The scan was processed for lithium disilicate crown fabrication.
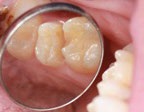
Figure 4—The occlusal reduction was completed using an egg-shaped NeoDiamond 1900F, and a NeoDiamond 0816.6CS flat-end taper shorty diamond was used to create a circumferential margin.
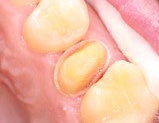
Figure 5—The preparation was polished and finished using a NeoDiamond 3314.10VF pointed cone diamond.
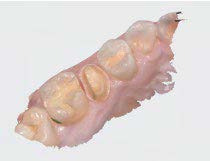
Figure 6—Digital impression showing preparation and opposing arch. The NeoBurr 331 carbide and NeoDiamond 1900F were used to achieve proper occlusal clearance.
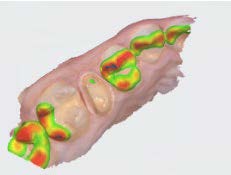
Figure 7—Digital impression showing preparation and opposing arch. The NeoBurr 331 carbide and NeoDiamond 1900F were used to achieve proper occlusal clearance.
Placing the Crown
At the time of final crown delivery, the NeoDiamond 3314.10VF finishing bur was used to adjust interproximal contacts, while the egg-shaped NeoDiamond was used to complete appropriate occlusal adjustments. The crown was then polished using a combination of ceramic polishing wheels. When the patient reported satisfaction with the fit, feel, and appearance of the crown, the internal aspect of the crown was air-abraded and prepared for bonding.The crown was bonded to tooth No. 4, and the tooth was subsequently cleaned with a microbrush and dental floss. After occlusion was verified, the patient was dismissed and was satisfied with her treatment and clinical outcome.
Durable, Disposable Diamonds & Carbides
Throughout my time as a dental clinician, I have had the opportunity to work with a variety of dental burs. Microcopy creates convenient, individually packaged, disposable sets of burs to fit my daily needs. Each bur is clearly color coded and labeled, which makes for easy identification. The company provides a wide variety of both diamond and carbide burs for every type of restorative dental procedure. I have never had any of the burs break during use and the diamonds rarely need to be replaced due to loss of grit. Overall, Microcopy has created an ideal set of dental restorative burs.

After graduating from The University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Dr. Derek Vinkovich completed
his General Practice Residency at Akron City Hospital in Akron, OH. He is an active member of Spear Study Clubs
and maintains a private practice in North Royalton, OH, where he takes a special interest in using CAD/
CAM technology to provide optimal care to his patients.
Microcopy
P.O. Box 2017
Kennesaw, Ga 30156-9017
P: 800.235.1863
F: 770.423.4996

011M (Ball) 25 Pack
QTY: 2
X
$97.00

011M (Ball) 25 Pack
QTY: 2
X
$97.00
STANDARD TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE
SPECIAL EXPORT TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE
RETURNS POLICY
Microcopy will accept returns from US and Canada direct customers once an approved Return Authorization number has been recorded. All returns older than 1 year will require a 15% restocking charge. No returns will be accepted after 3 years from original ship date. All shipment of goods outside of the continental US is final.
REMOVE

0110M (1)
Medium Grit
25/PK
$48.50
Reference F/G | 801-018 |
Head Diameter | 1.8 mm |
Head Length | 1.6 mm |
Overall Length | 19.2 mm |
Reference F/G
801-018
Head Diameter
1.8 mm
Head Length
1.6 mm
Overall Length
19.2 mm
No other grits offered for this shape
REMOVE

0112M (2)
Medium Grit
25/PK
$48.50
Reference F/G | 801-018 |
Head Diameter | 1.8 mm |
Head Length | 1.6 mm |
Overall Length | 19.2 mm |
Reference F/G
801-018
Head Diameter
1.8 mm
Head Length
1.6 mm
Overall Length
19.2 mm
No other grits offered for this shape
REMOVE

0116C (4)
Coarse Grit
25/PK
$48.50
Reference F/G | 801-018 |
Head Diameter | 1.8 mm |
Head Length | 1.6 mm |
Overall Length | 19.2 mm |
Reference F/G
801-018
Head Diameter
1.8 mm
Head Length
1.6 mm
Overall Length
19.2 mm
Medium (0116M)
![]() Bridge/Operative
Bridge/Operative![]() Ball
Ball![]() Beveled Cylinder
Beveled Cylinder![]() Dbl Inverted Cone
Dbl Inverted Cone![]() Egg
Egg![]() End Cutter
End Cutter![]() Flame
Flame![]() Flat End Cylinder
Flat End Cylinder
![]() Flat End Taper
Flat End Taper
![]() Mod. Flat End Cylinder
Mod. Flat End Cylinder
![]() Interproximal
Interproximal
![]() Football
Football
![]() Gross Reduction
Gross Reduction
![]() Inverted Cone
Inverted Cone
![]() Mod. Bevedled Cylinder
Mod. Bevedled Cylinder
![]() Mod. Flat End Taper
Mod. Flat End Taper
![]() Occlusal Reduction
Occlusal Reduction
![]() Pear
Pear
![]() Occlusal Reduction
Occlusal Reduction
![]() Depth Cutter
Depth Cutter
![]() Endo
Endo
![]() End Cutting
End Cutting
![]() Finishing
Finishing
![]() Guide-Pin
Guide-Pin
![]() NeoSpiral
NeoSpiral

0110M (1)
Medium Grit
25/pk
$48.50